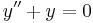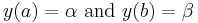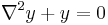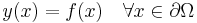Dirichlet boundary condition
In mathematics, the Dirichlet (or first-type) boundary condition is a type of boundary condition, named after Johann Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet (1805–1859).[1] When imposed on an ordinary or a partial differential equation, it specifies the values a solution needs to take on the boundary of the domain. The question of finding solutions to such equations is known as the Dirichlet problem.
- For an ordinary differential equation, for instance:
the Dirichlet boundary conditions on the interval ![[a, \, b]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/d2524b9940ce1c636bfb26ae09a941d2.png) take the form:
take the form:
where 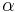 and
and 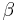 are given numbers.
are given numbers.
- For a partial differential equation, for instance:
where 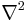 denotes the Laplacian, the Dirichlet boundary conditions on a domain
denotes the Laplacian, the Dirichlet boundary conditions on a domain 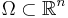 take the form:
take the form:
where f is a known function defined on the boundary 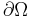 .
.
Many other boundary conditions are possible. For example, there is the Cauchy boundary condition, or the mixed boundary condition which is a combination of the Dirichlet and Neumann conditions.
See also
- Neumann boundary condition
- Mixed boundary condition
- Robin boundary condition
- Cauchy boundary condition
References
- ^ Cheng, A. and D. T. Cheng (2005). Heritage and early history of the boundary element method, Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements, 29, 268–302.